
1969
The data center has been authorized to advance the automation of bank accounting for a large group of Raiffeisen banks. At this time well-known and reliable magnetic ledger-card computers (MKC) were soon to be replaced by central computer systems.

1969
The foundation of centralized electronic data processing (EDP) has been laid on 28 December by computerising the accounting of Raiffeisenbank Vienna.
1969
At a time, electronic calculators had a hint of mysticism the first Raiffeisen banks proved to be innovative pioneers in data processing. By the end of 1970 already 9 Raiffeisen banks have switched to EDP.

1970
A time when data had a representational effect and people built a personal relationship to valuable data.
1970
Even data transports – literally a man going by train – have been also put to the acid test. Test transports have been carried out with old newspapers in a briefcase.

1970
The IBM 370/145 was the first commercial computer system which memory consisted of semiconductors. Its size characterized the need for space of many technology companies.
1970
Only two years after the foundation of Raiffeisen Informatik (former Raiffeisen Rechenzentrum) the solid development allowed for a major investment: namely the high-performing computer system IBM 360/20 with 16 KB RAM.
The new technical centrepiece of the company enables quite comfortable programming in machine-oriented languages.

1971
Without any knowledge of the breath-taking development in the mid-90s, the first programmes for online-accounting have been developed.
1971
The online age is already anticipated in this early stage. Raiffeisen banks and 10 Lagerhaus cooperatives have switched to EDP.

1972
A unique account number (including check digits) has been introduced against all odds of federal customary– from Feldkirch to Eisenstadt.
1972
This hard-fought-for unity lasts till today and stands for a non-recurring expense generating a substantial simplification.

1973
Pioneering days are unconventional times. It was also true in the times of RRZ when faithful operators were staying in system rooms for 72 hours without any break.
1973
Times when camp beds where set up in the warm exhaust air of computers. Times when complicated part of maintaining social contacts – according to own statements of company management – had to be practiced now and then in sips.

1974
COM was installed as a new output medium in RRZ, so Microfiche had its appearance. Its comfortable consequence was a massive reduction of paper output. Despite gaining space the increasing demand for space justified the relocation to Raiffeisenhaus Vienna.
1974
While during the founding years a simple accounting program consisted of a huge batch of punch cards, physical stack of paper for the pure data transformation reached an impressive height. Some compared it with the height of St. Stephen’s Cathedral in Vienna. The Microfiche reached its zenith with 95 million pages on 800,000 Microfiche. Still today the COM technology is used in special cases for physical data backup.

1975
In the era of remote data transmission via telephone dial-up lines Raiffeisenbank Vienna received a comprehensive online service bundle.
1975
At the beginning the Securities department was selected with four enquiry services for the time being. The required time for performance monitoring improved from almost one day to seconds.

1977
The SWIFT (Achtung: richtige Schreibweise im deutschen Text beachten) terminal of the Austrian Raiffeisen sector has been installed in the RRZ.
1977
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) provides a network that enables financial institutions worldwide to send and receive information about financial transactions in a secure, standardized and reliable environment.
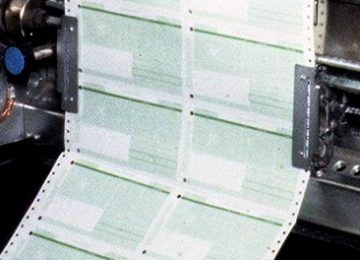
1978
The account statements of Raiffeisenbank have been revised to place more information on the statements. To find a common solution was not an easy task.
1978
Despite all obstacles a nation-wide design has been implemented. Until this point customers had to face different shapes and sizes of their bank statement with each change in the booking system.

1979
After a large fire in the OeNB (Austrian Central Bank) the RRZ accommodated the electronic data collection of OeNB which restored their EDP operations within a few days.
1979
RRZ has taken internal actions to increase data security in line with the new data protection law of 1980. The security committee of RRZ has been established to activate control mechanisms through organizational and EDP-technical measures. To guarantee the quickest recovery of the data center in case of any incidents.
